Smart Integration Connector Setup
You must set up Smart Integration Connector in this order:
-
Install the OneStream Smart Integration Connector Local Gateway Server (OneStreamSmartIntegrationConnectorGateway.msi) on a Windows Server 2019+ in your environment.
-
Create a Gateway in the OneStream Windows application to connect OneStream Cloud instance to a Local Gateway.
-
Export the gateway configuration and import this configuration to the Gateway Settings in the OneStream Local Gateway Configuration.
-
For gateways of type Database Connection, to allow connections to local databases,
-
Define a Local Gateway connection including Data Sources through the OneStream Local Gateway Configuration.
-
Test any configured Data Sources to confirm they are communicating properly.
Note that testing direct connections may involve building test business rules to perform proper validation. -
Define a custom database connection in the OneStream System Configuration Setup.
-
When installation is complete, you can access remote data sources using business rules, member formulas, or dashboard data adapters in OneStream through the Smart Integration Connector.
Gateway Terms
The Smart Integration fields define the gateway. You can find more information about this below.
| Relay Name | Refers to the internal namespace of the relay service that is responsible for managing the data flow for all defined Gateways. For example, arn-mysite.servicebus.windows.net. |
| IPv4 Whitelist | Contains the list of IPs or CIDR addresses that are allowed to transfer data via SIC. |
| Name |
The name of the gateway. Gateway names are completely arbitrary and typically refer to the region (North East) or data source such as (SAP). NOTE: The gateway name cannot be changed once created and they must be unique across all environments--both development and production. You can delete an existing gateway and recreate it with a new name. |
| Description | Text describing the role and purpose for the gateway and the data sources to which it is connecting. |
| Gateway Server Name | This is the name of the gateway Server that the gateway is associated with. Select an existing gateway server or enter a new one. |
| Web API Key (Database Connections only) |
This is an editable field. You can change your key as needed. If changed, it must also be changed in the Smart Integration Connector Local Gateway Server. It is designed to offer an additional layer of protection within your network when invoking APIs embedded in the Smart Integration Connector Local Gateway Server. The purpose of the Web API Key is to give you full control on who can access the data sources in your network. |
| Gateway Key | This is the cloud-key used to authenticate the Smart Integration Connector gateway to the customer OneStream environment. This key can be rotated in the OneStream Application by Smart Integration Connector Gateway administrators and must be the same in both the remote Gateway service and in OneStream. |
| Status | Value will be Online if the local gateway is running and returning heartbeat messages back to OneStream. If the Smart Integration Connector Local Gateway Server is unavailable, stopped, or network connectivity is interrupted, it will display Offline. |
Status Indicators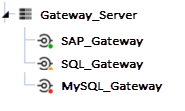 |
Status indicators give a visual notification based on the Gateway status. An indicator turns green on the side menu if the Gateway is Online, red if the Gateway is Offline, and yellow if the Gateway is Offline but there is a newer version of the Local Gateway Server available. For Direct Connections, the yellow status should never display. |
| Instance Count | Displays the count of active gateways. Grayed out by default. While this value is typically 1 when the gateway is online, you may have a listener count of two or more if there are redundant active gateways for high availability. By default, OneStream allows a total of five active gateways per environment. This can be increased by contacting support. |
|
Version (Database Connections Only) |
Displays the Smart Integration Connector Local Gateway Server version. This version may be different from the deployed version of OneStream and allows administrators to observe and monitor versions of Smart Integration Connector Gateway software deployed. |
| Bound Port at Gateway | Remote port bound to Gateway endpoint. Relational Database Gateways should default to 20433 while direct connections allow any port running on a remote host to be used. |
|
Remote Gateway Host (Direct Connections Only) |
Remote port host to Gateway Server. Used if surfacing an endpoint such as an SFTP Server. This could be the hostname or IP address on the network that the Gateway Server resides in. example: 172.168.4.7 or sftp.mycompany.com |
|
Bound Port in OneStream (Direct Connections Only) |
This is an optional customer defined port that can be referenced in data management or business rules to directly access services such as sFTP and WebAPI. This must be a globally unique port in a OneStream deployment per direct connection and should be a TCP port number > 1024 and <65535. When creating the gateway, use the default of -1 and OneStream will automatically assign an open port. |
| Gateway failures reporting interval (min) | Minutes to wait between reporting gateway failures into the OneStream Error Log. The default is five minutes and the max is 1440 minutes. If a gateway is unreachable, an item is put in the error log using this interval value in minutes and can be adjusted. |
Local Gateway Server Installation
Smart Integration Connector is available in OneStream from the System > Administration tab.
-
Download the Smart Integration Connector install (OneStream_Connector_#.#.#.zip) file from the Platform section of the Solution Exchange.
-
Copy the Smart Integration Connector Local Gateway Server installer to a Windows Server within your environment.
-
Run the installer as an administrator. Accept all the default prompts. When completed, the Local Gateway Server will be installed on your Windows Server.
IMPORTANT: If you are upgrading, you must follow steps 4-7.
-
Run the OneStream Local Gateway Configuration Utility.
-
The XFGatewayConfiguration.xml file will open by default.
IMPORTANT: Do not change the name of the XFGatewayConfiguration.xml file. The OneStream Smart Integration Connector Gateway Service only references this XFGatewayConfiguration.xml file upon start-up. The Save As functionality is used to create a backup of the file. Do not rename, move, or change the location of the XFGatewayConfiguration.xml file.
-
Save the configuration file.
-
Follow the dialog box and restart the service.
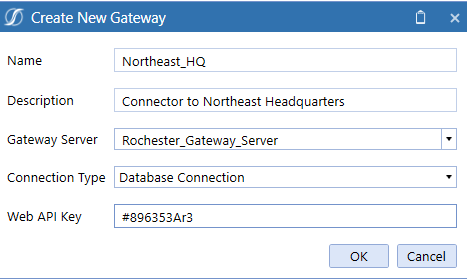
Create a New Gateway
Gateways are used to connect OneStream to the Smart Integration Connector Local Gateway Server over the Azure Relay. You will establish whether the gateway is a direct or database connection. After the gateway is created, you will need to copy the configuration to the Smart Integration Connector Local Gateway Server using the OneStream Local Gateway Configuration.
-
Go to System > Administration > Smart Integration Connector.
-
Click
 Create New Gateway.
Create New Gateway. -
Enter the Name and Description. For descriptions of the fields in steps 3-6, refer to the Gateway Information section.
-
Select the Gateway Server from the drop-down, or enter a new Gateway Server name.
-
From Connection Type, select a Database Connection or Direct Connection. You will have to enter different information depending on the connection type you select.
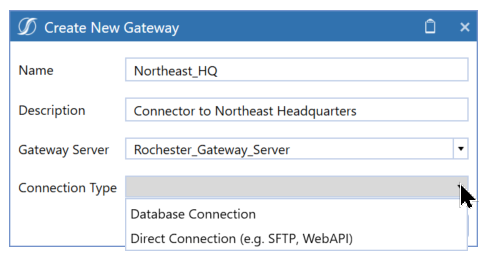
NOTE: The Gateway name cannot be changed once created and must be deleted and re-created.
Create a Database Connection
A database connection is used to connect to relational databases such as SQL Server, MySQL, etc. using ODBC, OleDB or .NET drivers and is also necessary for remote Smart Integration Functions to execute. It is recommended to have at least one Database connection endpoint per Gateway Server even if relational databases will not be accessed by OneStream. The Local Gateway Configuration Utility facilitates configuration of required credentials for associated local gateway. The identification of a local gateway connection must correspond to a custom database connection established to the OneStream Application Server.
After you create a new gateway, you can complete the database connection by following these steps:
-
From Connection Type, select Database Connection. For descriptions of the fields in steps 1 and 2, refer to the Gateway Information section.
-
Enter a Web API Key.
NOTE: The Web API Key is used as an additional layer of security when communicating with the Smart Integration Connector Local Gateway Server internal APIs. WebAPI keys are not required, but recommended to enhance security and can be modified or added at anytime. The Local Gateway Service introduces a WebAPI exposed only to OneStream and bound only to localhost on the server it is deployed to. This WebAPI is inaccessible on the remote network. If the Local Gateway Service is bound to other network interfaces, it's suggested to use the WebAPI as a mechanism to enhance security on the remote network preventing unauthorized use of OneStream WebAPIs.
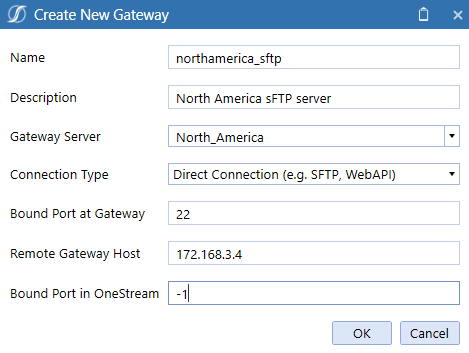
Create a Direct Connection
A gateway direct connection represents a point-to-point channel to specific remote network resources such as an sFTP server or Web API (including iPaaS services).
NOTE: It is required to have at least one Database connection to use a Direct Connection as the database connection is used to monitor the availability of the remote Smart Integration Connector Gateway server.
The existence of a database connection does not necessarily mean it must be used or configured if only Direct Connections are desired.
After you create a new gateway, you can configure the direct connection by following these steps:
-
From Connection Type, select Direct Connection (e.g, SFTP, WebAPI). For descriptions of the fields in steps 1-4, refer to the Gateway Information section.
-
Enter the Bound Port at Gateway. This port represents the well-known TCP service to expose from an on-premises host such as sFTP which would equate to port 22.
NOTE: Note that the remote service port is required to configure the connection and may require consultation with network or IT resources to obtain. It is also required that any firewalls between the Local Gateway Server and the remote host allows traffic to the destination port specified.
-
Enter the Remote Gateway Host (for example, localhost). This represents the remote host name or IP address accessible by the OneStream Smart Integration Connector Local Gateway Server. If the host or IP address is accessible or resolvable from the OneStream Smart Integration Connector Gateway service, or using remote resources accessible through on-premises WAN, it can be exposed for use.
-
Enter a Bound Port in OneStream. It is recommended to use -1 for this value as the OneStream application servers will locate an unused and available port to map to this connection This port number must be globally unique across all application servers in a OneStream deployment and care should be taken if a specific port is specified. This is the port that is then used to access the remote host via business rules, data management jobs, and so on. from OneStream application servers to allow network traffic to traverse to the remote host and port.
-
Using this direct connection in OneStream is done by accessing localhost: [Bound Port In OneStream] which will tunnel traffic back to the configured remote Gateway Host to the configured bound port at gateway.
-
Example: Remote sFTP server at 172.168.3.4 listening on port 22.
-
Bound Port in OneStream is configured as port 45000. Note that when -1 is used, the selected port number is available/displayed after saving and also surfaced in the OneStream Error Log.
-
In OneStream Business Rules, you can access the remote host by connecting to localhost:45000.
-
In a OneStream Business Rule, this port can also be obtained in code allowing this port number to be changed without updating Business Rules:
CopyDim gatewayDetails As GatewayDetails = BRApi.Utilities.GetGatewayConnectionInfo(si, "northamerica_sftp")
Dim remotePort = gatewayDetails.OneStreamPortNumber
-
Export and Import the Gateway Configuration
You must copy the gateway configuration settings and paste them into your Smart Integration Connector Gateway to establish the connection.
-
Go to System > Administration > Smart Integration Connector.
-
Select the Gateway to export.
-
Click
 Export Gateway Configuration. The Gateway Configuration Details are copied to the clipboard.
Export Gateway Configuration. The Gateway Configuration Details are copied to the clipboard.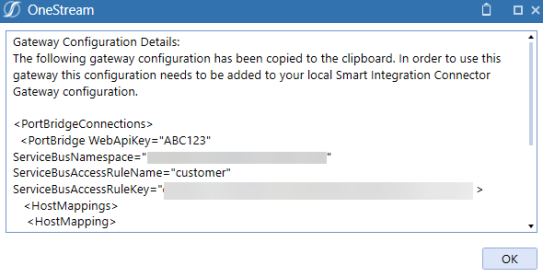
-
On your Windows Server, open the OneStream Local Gateway Configuration. This runs as administrator by default.
-
Click
 next to Local Gateway Settings.
next to Local Gateway Settings.
-
Click
 next to Local Gateways.
next to Local Gateways.
-
Import
 the previously copied Gateway Configuration.
the previously copied Gateway Configuration.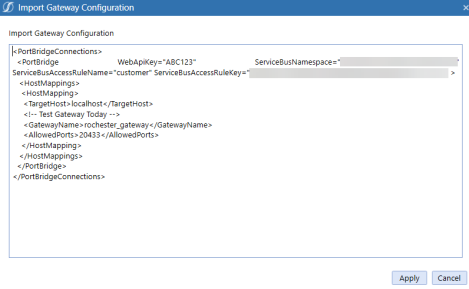
-
Click Apply.
-
Click Test Connection to test the connection.
-
Click OK twice.
-
Save the configuration.
-
Click Yes to apply the changes and restart the Local Gateway Server.
New Gateway Key Generation
Smart Integration Connector administrators can rotate the Gateway Key maintained by the underlying cloud service, however it must be the same for both the Smart Integration Connector local gateway and the gateway configuration to function properly.
-
Select an existing gateway.
-
Click Regenerate Gateway Key for Selected Gateway.
-
You must re-export your Gateway Configuration and apply the new settings through the OneStream Local Gateway Configuration.
-
Click OK.
Create a Local Gateway Connection to a Data Source
A data source contains the name, connection string, and database provider for the database of your choice. You can set up a PostgreSQL, SQL, Oracle, OleDb, MySQL, ODP.net, or Microsoft ODBC connection here. The data source is configured using the Local Gateway Configuration Utility. The utility was installed as part of the Smart Integration Connector Local Gateway install.
-
Start the OneStream Local Gateway Configuration.
-
Click
 to configure Local Gateway Connections details to set up the Data Sources to local databases, APIs, or other on-premises resources.
to configure Local Gateway Connections details to set up the Data Sources to local databases, APIs, or other on-premises resources.
-
Click
 next to Data Sources.
next to Data Sources.
-
Click
 Add Item to add a new data source.
Add Item to add a new data source.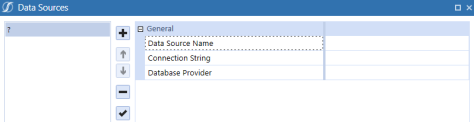
-
Enter the Data Source Name, Connection String, and select a Database Provider. You can add as many data sources as necessary. The Data Source Name must be unique for each connection defined within a specific OneStream Smart Integration Connector Local Gateway Server. Names can be re-used across deployed instances of the Windows Service across your network. See the examples below for connection string examples to a variety of relational data sources such as PostgreSQL, SQL, and ODBC, and Oracle. Connection Strings are encrypted automatically. You can edit the plain text string by clicking the ellipsis.
NOTE: Oracle databases require drivers and specific configuration provided by Oracle.
-
Click OK to save your configuration.
NOTE: The connection strings below include user IDs and passwords. If Integrated security is desired, you can configure the OneStream Smart Integration Connector Gateway Service to run under a specific service account versus saving usernames and passwords in connection strings.
Microsoft SQL Server
Below is an example for setting up a SQL database using the SqlClient provider.
-
Click
 next to Data Sources.
next to Data Sources. -
Click
 Add Item to add the data source.
Add Item to add the data source. -
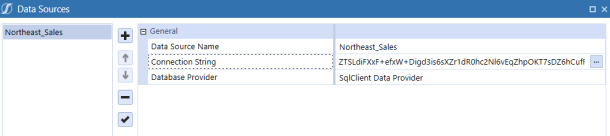
Data Source Name: Northeast_Sales
-
Connection String:
with UserID / Password: Data Source=localhost;Initial Catalog=Sales_DB;Persist Security Info=True;User ID=sa;Password=*****;Max Pool Size=1000;Connect Timeout=60;
using Integrated Security: Data Source=localhost;Initial Catalog=Sales_DB;Trusted_Connection=True; -
From Database Provider, select SqlClient Data Provider.
-
Click Test Connection to test the data source.
-
Click OK to save.
MySQL Data Provider
Below is an example for setting up a MySQL Data Provider.
-
Click
 next to Data Sources.
next to Data Sources. -
Click
 Add Item to add a new data source.
Add Item to add a new data source. -
Data Source Name: Sales_UK
-
Connection String: Server = localhost;Port=3306;uid=root;pwd=Onestream123!;database=gatewaymysql;
-
From Database Provider, select MySQL Data Provider.
-
Click
 Test Connection to test the data source.
Test Connection to test the data source. -
Click OK to save.
Oracle Database Examples
Connecting to Oracle requires the download and configuration of the Oracle Data Access Components (ODAC) obtained directly from Oracle’s website. Follow the steps below to get access to these drivers and files.
-
Go to the latest web page for Oracle .NET and Visual Studio ODAC Downloads for Oracle Database.
-
After installation, the ODP.NET Provider will display as an available Database Provider in the utility when adding a new data source.
-
The connection string for Oracle databases can be set up to either reference or require a locally defined tnsnames.ora file for the requested data sources.
Example Connection Strings:
-
Oracle Data Provider for .NET: Data Source=oracletest;User Id=OneStream1;Password=*********;
-
Oracle Data Provider without TNSNames.ora: Data Source=(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS_LIST=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=MyHost)(PORT=MyPort)))(CONNECT_DATA=(SERVER=DEDICATED)(SERVICE_NAME=MyOracleSID))); User Id=myUsername;Password=myPassword;
OracleClient Database Provider
Below is an example for setting up a OracleClient database provider.
-
Click
 next to Data Sources.
next to Data Sources. -
Click
 Add Item to add the data source.
Add Item to add the data source. -
Data Source Name: Sales_EMEA
-
Connection String: Data Source=oracletest;User Id=OneStream1;Password=********
-
From Database Provider, select OracleClient Data Provider.
-
Click
 Test Connection to test the data source.
Test Connection to test the data source. -
Click OK to save.
Oracle Data Provider for .NET
Below is an example for setting up a Oracle Data Provider for .NET.
-
Click
 next to Data Sources.
next to Data Sources. -
Data Source Name: Sales_SouthAmerica
-
Connection String: Data Source=oracletest;User Id=OneStream1;Password=********
-
From Database Provider, select Oracle Data Provider for .NET.
-
Click
 Add Item to add a new data source.
Add Item to add a new data source. -
Click
 Test Connection to test the data source.
Test Connection to test the data source. -
Click OK to save.
PostgreSQL (Npgsql Data Provider)
Below is an example for setting up a PostGres database.
-
Click
 next to Data Sources.
next to Data Sources. -
Click
 Add Item to add the data source.
Add Item to add the data source. -
Data Source Name: RevenueMgmtPostGres
-
Connection String: Server=localhost;Port=5432;Database=revmgt;User Id=onestream;Password=********;
-
From Database Provider, select Npgsql Data Provider.
-
Click
 Test Connection to test the data source.
Test Connection to test the data source. -
Click OK to save.

OleDb Data Provider
Below is an example for setting up an Oracle database. This does not require additional download and configurations.
-
Click
 next to Data Sources.
next to Data Sources. -
Click
 Add Item to add the data source.
Add Item to add the data source. -
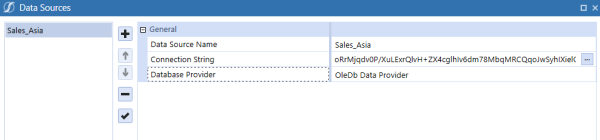
Data Source Name: Sales_Asia
-
Connection String: Provider=OraOLEDB.Oracle;Data Source=localhost:1521/XE;Initial Catalog=myDataBase;User Id=myUsername;Password=********;
-
From Database Provider, select OleDb Data Provider.
-
Click
 Test Connection to test the data source.
Test Connection to test the data source. -
Click OK to save.
ODBC Data Provider
Below is an example for setting up a ODBC data source for Oracle.
-
Click
 next to Data Sources.
next to Data Sources. -
Click
 Add Item to add the data source.
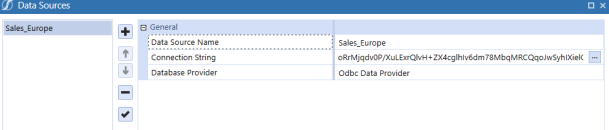
Add Item to add the data source. - Data Source Name: Sales_Europe
-
Connection String: Driver={Microsoft ODBC for Oracle};Server=(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=199.199.199.199)(PORT=1523))(CONNECT_DATA=(SID=dbName)));Uid=myUsername;Pwd=myPassword;
-
From Database Provider , select Odbc Data Provider.
-
Click
 Test Connection to test the data source.
Test Connection to test the data source. -
Click OK to create the new source
-
Click Save.
(Optional) Remove UserID and Passwords by Integrated Security
You can remove plain text UserID and Passwords from connection strings in Smart Integration Connector if your organization has concerns over credential storage in the Smart Integration Connector Gateway configuration file. This requires running the Windows Service under a Service Account identity and using integrated security to connect to remote data sources which eliminates local storage of any plain-text credentials. Additionally, ODBC data sources can be defined (using a system DNS) to remove credentials from the configuration file.
Update the Local Gateway Connection String
-
Open your OneStream Local Gateway Configuration.
-
Open a Local Gateway Connection.
-
Navigate to the Connection String and use an Integrated or Trusted Security string. For example: Data Source=localhost,Initial Catalog=OneStream_GolfStreamDemo_2022;Trusted_Connection=True;
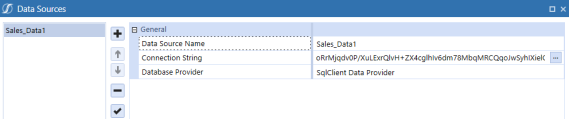
NOTE: Trusted Connections use the UserID and password you use to log into the Windows Server.
NOTE: The example above is for SQL server. Trusted connections vary by Data Provider type.
-
Click OK.
-
Save your Data Source.
Update Permissions on the Service
Next, you need to update the service to run as the user. If the service is not updated, the connection does not update and errors will occur.
-
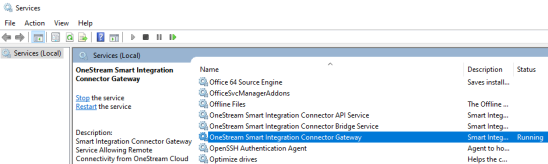
Open Windows Services.
-
Navigate to OneStream Smart Integration Connector Gateway. The service should be running.
-
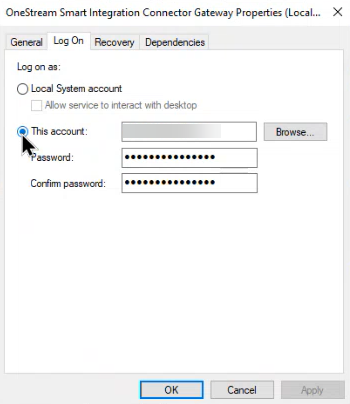
Right-click and open Properties.
-
Click the Log On tab. Typically, this will default to the Local System account.
IMPORTANT: Before moving on to the next step, ensure that you have the appropriate permissions and approvals from your IT Administrators to complete the Log On change. You may need to access Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio to verify permissions.
-
Change this from Local System account to This account and enter your domain and/or login that has access to the datasource. Depending on how your SSO is configured, your account could require your domain name, UserID, and password. Contact your IT Administrator if you have questions on your account domain.
-
Click Apply.
-
Click OK.
-
Right-click and select Restart to restart and update the service.
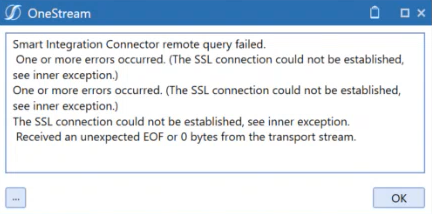
Test the Updated Integrated Connection String
You should test your connection through a Data Adapter query to verify your access to Smart Integration connector. An alternate SQL Query to pulling the first 10-50 rows is sufficient. See Data Adapters Example.
Test the Gateway
-
You can test the gateway by double-clicking the OneStreamGatewayService.exe file located in the installation folder.
NOTE: The Smart Integration Connector Gateway Windows Service must be in a stopped state to run in the console for test purposes.
The following command window is displayed: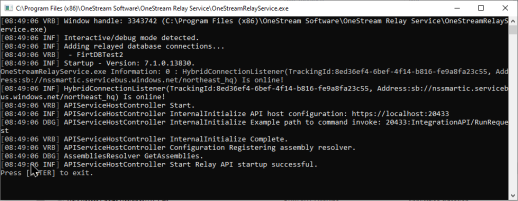
-
Correct any errors that are displayed in the command window.
-
In the OneStream Windows Application client, refresh Gateway Details from System > Administration > Smart Integration Connector > Your gateway.
-
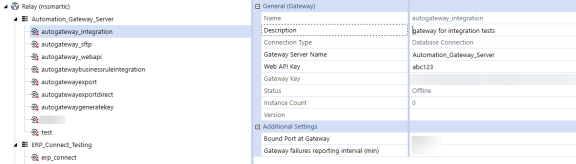
You should see the Instance Count change from 0 to 1,
-
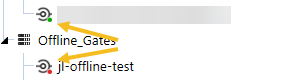
The Status change from Offline to Online. Additionally, status indictators turns green on the side menu if the Gateway is Online, red if the Gateway is Offline, and yellow if the Gateway is Offline but there is a newer version of the Local Gateway Server available. See the second screenshot under this step for a close up of the indicators.
-
The Version field will show the version of the running Smart Integration Connector Gateway.
-
-
Press Enter twice on the keyboard to stop the service in the command window and then close the command window.
Restart OneStream Smart Integration Connector Gateway
After communication has been verified, the following Windows Service needs to run in order to maintain communication with the OneStream Cloud instance. By default, these services are set to start after a Windows reboot. You can also manually start them using the Windows Service control manager or the command line using the net start/net stop commands. If you're having issues restarting the service, refer to Troubleshooting.
-
Open the OneStream Local Gateway Configuration.
-
Click Tools > Restart OneStream Smart Integration Connector Gateway.

Redundant and Fail-over Gateways
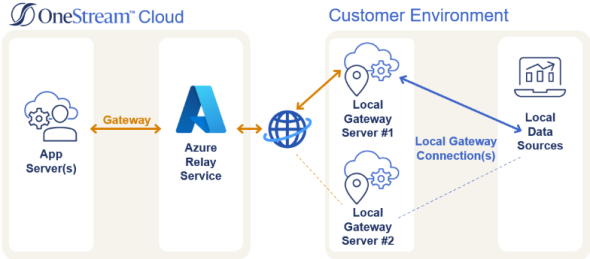
The Smart Integration Connector Local Gateway Server can be installed on a separate Windows Server to operate as a fail-over. The Local Gateway Server Gateway establishes connection to the Relay that becomes the ac/primary Local Gateway Server instance while the second Local Gateway Server environment remains idle until the primary goes offline. The second Local Gateway Server Gateway would be the fail-over in this scenario and automatically accept traffic if the primary server instance were to go offline.
-
-
Since the Data Source Connection Strings are encrypted, you will need to re-enter the connection string for each Data Source.
-
Click Tools > Local Gateway Connections > Data Sources.
-
Select a Data Source and select the Connection String.
-
Select OK to provide a new connection string.
-
Delete the encrypted text and replace it with a valid connection string from the primary server.
-
Select OK to encrypt the connection string and close the dialog box.
-
Repeat steps A through F for all the remaining data sources.
-
Click OK to close the Data Sources.
-
Click OK to close the Local Gateway Connections.
-
Click Save to save the Local Gateway Configuration.
-
Click Yes to restart the service.
-
-
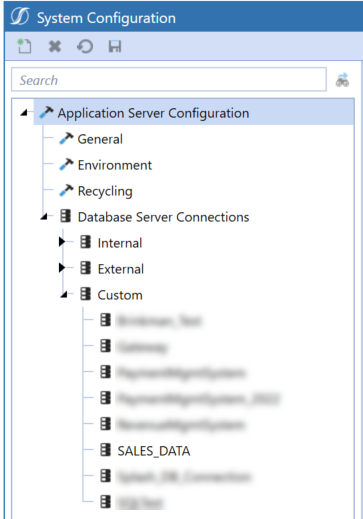
Define Custom Database Connections in OneStream System Configuration Setup
Now that the gateway is set up and communicating with the Smart Integration Connector Gateway, the final step is to set up the location of the remote data source in OneStream. To continue adding the Custom Database Connection, you must assign a user to the ManageSystemConfiguration role.
-
Go to System > Administration > System Configuration.
-
Select Application Server Configuration > Database Server Connections.

-
Select
 Create Item to create a new Custom database server connection.
Create Item to create a new Custom database server connection.NOTE: If the only fields displayed are Name and External Database properties, verify that the current user is assigned to the ManageSystemConfiguration role.
-
Enter the Name of the Database Server Connection.
-
For Database Provider Type, select Gateway.
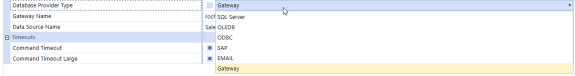
-
The Gateway Name drop-down menu will be populated with a list of configured Gateways. Select the Gateway.
-
After the Gateway is selected, the Data Source Name drop-down menu populates with a list of the Local Gateway Server Database Connections.
-
Select a Database Connection from the drop-down menu.
NOTE: If the remote data source is not displayed or the Gateway is offline, you can select Custom to allow the data source to be manually specified.
-
Click Save to complete the configuration.
-
Verify the customer database connection is under Custom.